How to protect yourself when interest rates rise
If you plan to borrow money, you may be charged interest. So, it’s important to understand how interest rates can impact the overall cost of borrowing.
Interest is set by the lender. When you use credit, you pay back the borrowed amount, known as the principal, plus interest. This happens over a defined period of time.
An interest rate hike (increase) can make it more expensive to borrow money, meaning your loan payments could rise if:
- You have a mortgage, line of credit or loan with a variable interest rate
- It’s time to renew your fixed-rate mortgage or loan
The ABCs of interest rates
Before we dive into how you can protect yourself before interest rates rise, let’s go over some basics.
How are interest rates determined?
Your interest rate depends on a variety of factors, including your loan amount, the loan type and your credit score.
Improving your credit score could help you get a lower interest rate. This could translate into smaller monthly payments and paying less interest costs to borrow money. Learn how you can boost your credit score today.
Fixed and variable interest rate loans
Your lender may offer you a choice between a fixed or variable interest rate loan. Let’s break down the two types.
Fixed interest rate loans
Fixed-rate loans lock in your interest rate for the term of your loan.
The term is the length of the payback period. Loan terms, for example, could range from 12 months to seven years. This gives you the flexibility to help meet your monthly budget and find a payment you can afford.
With fixed-rate loans, you’ll know exactly how much principal and interest you’ll be paying with each regular payment during your borrowing term. With a fixed-rate loan, you’ll know when you’ll have fully repaid your debt.
Variable interest rate loans
Variable interest rates are usually affected by the prime rate. They go up or down when the prime rate changes. If the variable interest rate decreases, more of your payment goes towards the principal and you’ll pay off your loan faster.
Depending on your loan agreement, your payments could increase when rates go up. Or they could remain the same, but the time it takes to pay back your loan may increase. If you’re unsure, check with your lender before signing.
The prime rate is set by your lender and is influenced by the Bank of Canada’s interest rate. The Bank of Canada is Canada’s central bank.
There’s typically a domino effect when the Bank of Canada changes its interest rate. Most lenders will adjust their prime rate after the Bank of Canada changes its interest rate.
Variable interest rates are typically expressed as prime plus or minus a certain percentage. They’re usually lower than fixed interest rates, in part because they can be riskier for borrowers.
Source: Protecting yourself if interest rates rise, Financial Consumer Agency of Canada.
When do rates rise and fall?
If the economy is growing too fast, you may see a rate increase to keep inflation from rising above the target. The Bank of Canada aims to maintain inflation close to 2%. And if the economy is struggling to grow, you may see rates drop to keep inflation from falling below the target.
Inflation is a measure of how much prices for goods and services are increasing.
Source: Understanding our policy interest rate, Bank of Canada.
Choosing between a fixed or variable interest rate loan
Some people only consider the interest rate when deciding between a fixed or variable rate loan. But it’s not that simple. You should also consider your risk tolerance.
If you want the peace of mind that comes with knowing your interest rate and payment will stay the same for the full term, a fixed-rate loan might work. They can offer stability, which can help with long-term budgeting.
The downside is that you may not be able to take advantage of a lower interest rate once you have locked into a fixed term. Should interest rates drop during the term of your loan, you could be locked in at a higher interest rate and may not have the ability to have more of your payment cover the principal.
If you have a higher appetite for risk and you think rates will stay the same or decrease during the term of your loan, a variable-rate loan might work for your situation.
Before signing and accepting the terms of a variable interest rate loan, check with your lender to see if the loan payments will change when interest rates rise. If yes, you’ll need to consider if you can afford the payments if rates go up. You’ll also need to monitor the interest rate so you can manage your finances and adjust your budget accordingly.
Before you make a decision, take into account how you might feel about potential future changes in interest rates and payment amounts. It is recommended to consult a professional to assess your financial situation and tolerance.
Preparing for rising interest rates
Here are some things you can consider when preparing for an interest rate hike:
- Examine your budget and avoid overspending. Think about your needs and wants. Having more money to pay down your debt will help avoid financial stress later.
- Consider paying down debts with the highest interest rates first. This way, less money goes towards interest and you could be able to get out of debt sooner.
- Consider paying off higher interest rate retail credit cards or higher interest loans with a loan that has a lower interest rate.
- Avoid taking on more debt than you can realistically afford.
Source: Protecting yourself if interest rates rise, Financial Consumer Agency of Canada.
How higher rates may affect your variable interest rate loan
Let’s explore how two different variable rate loans are affected if rates move up.
Scenario 1: You have a variable interest loan agreement where your regular payment amount stays the same, when the Prime Rate changes
For this type of loan, if the interest rate goes up, your regular payment will remain unchanged but repaying your loan might take longer, since more of your payments will be going towards interest.
The one exception is in the case that interest rates rise to the point that your payment doesn’t cover the interest portion of the payment (known as the “trigger rate”). In this situation, you will have the option of increasing your regular payment amount going forward or making one or more supplementary payments to cover the difference.
Scenario 2: You have a variable interest rate loan agreement where the regular payment amount changes when the Prime Rate does
For this type of variable interest rate loan, if the interest rate goes up, your regular loan payment will also increase.
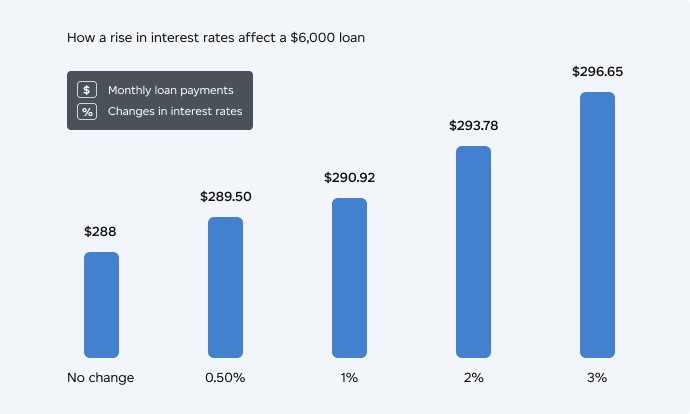
Let’s say you have a personal loan of $6,000 that you want to pay off in two years. Your current rate is 14% and your monthly payment – which is comprised of principal and interest – is $288. The chart below shows changes to your monthly payment if rates rise between 0.5% to 3%.
Not sure what kind of variable interest rate loan you have, or are considering? Check with your lender.
The bottom line
If an interest rate increase is on the horizon, it’s a good time to review your finances. Take steps to financially protect yourself and if you’re looking to borrow money, understand the cost of borrowing.
This material has been prepared for informational purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for obtaining advice from a financial professional.
Adapted with permission from the Financial Consumer Agency of Canada, 2022.